The war in the Pacific during World War II began with Japan’s military expansion and aggressive actions in the late 1930s and early 1940s. Here’s a brief overview of the events leading to the war:
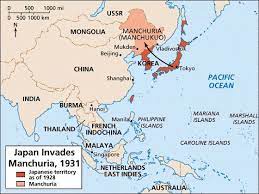
- Japanese Invasion of Manchuria (1931): Japan, seeking natural resources and territory, invaded Manchuria (northeastern China) and established the puppet state of Manchukuo.
- Second Sino-Japanese War (1937): The conflict escalated when Japan launched a full-scale invasion of China. The Imperial Japanese Army committed numerous atrocities during the occupation of Chinese territories.
- Tripartite Pact (1940): Japan signed the Tripartite Pact with Germany and Italy, forming the Axis Powers. This alliance solidified Japan’s alignment with the Axis and signalled a growing threat to the Allied powers.
- Invasion of French Indochina (1940-1941): Japan occupied French Indochina (Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia) to gain access to resources, particularly oil, rubber, and tin.
- Embargo and Economic Pressure: In response to Japan’s aggression, the United States, the United Kingdom, and other Western powers imposed economic sanctions and embargoes on Japan, particularly in regard to oil and steel exports.
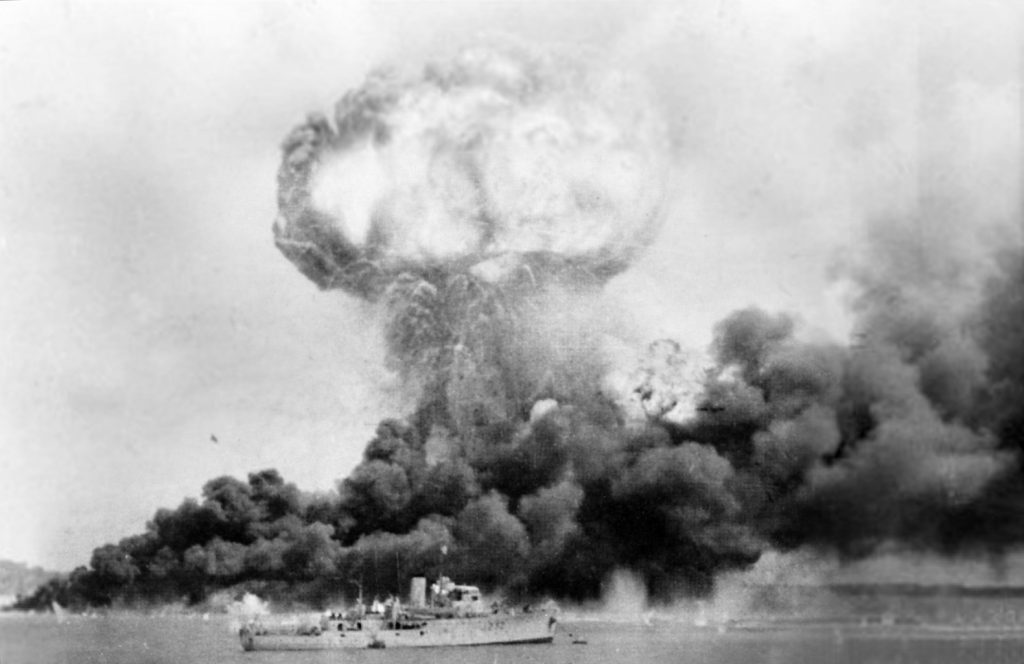
- Attack on Pearl Harbor (December 7, 1941): In an attempt to neutralise the threat posed by the U.S. Pacific Fleet, Japan launched a surprise attack on the U.S. naval base at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. This attack resulted in heavy losses for the U.S. Navy and brought the United States directly into the war.
- The Japanese occupation of the Netherlands East Indies in early 1942 and the bombing of Darwin and Broome.
Following the attack on Pearl Harbor, the war in the Pacific intensified, with Japan expanding its control over Southeast Asia, the Pacific islands, and parts of the Western Pacific. The United States, along with its allies, gradually turned the tide of the war through a series of military campaigns, island-hopping strategies, and naval battles, ultimately leading to Japan’s surrender in August 1945 after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.